People with diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are at high risk for kidney failure, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, and premature mortality.
The 2022 American Diabetes Association (ADA) Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes and the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease each provide evidence-based recommendations for management.
These recommendations included several medications with proven efficacy to reduce progression of CKD in patients with diabetes and Finerenone was one of them.
Finerenone
A mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, was approved by FDA in July 2021 to be used in chronic kidney disease associated with type 2 diabetes to reduce the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic kidney disease associated with type 2 diabetes.
How does it differ from other mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists?
spironolactone and eplerenone are steroidal MRAs but finerenone is a non-steroidal MRA
-
Spironolactone → Besides its use in heart failure and ascites, Spironolactone has antiandrogenic activity that leads to many of its off label uses, such as treatment of hirsutism, female pattern hair loss, and adult acne vulgaris
-
Eplerenone → Similar to spironolactone but it selectively binds to mineralocorticoid receptors relative to its binding to glucocorticoid, progesterone, and androgen receptors. So, gynecomastia and hyperkalemia are less likely with eplerenone than spironolactone.
-
Finerenone→ It is distributed relatively equally between the heart and the kidney (spironolactone and eplerenone have higher concentrations in renal tissue than in cardiac tissue). It binds selectively to mineralocorticoids receptors and it is at least as potent as spironolactone with lower incidence of hyperkalemia and other adverse effects compared with both spironolactone and eplerenone (no significant affinity or activity at androgen, progesterone, estrogen, and glucocorticoid receptors) .
Is there any monitoring or precautions while using this medication?
K level and eGFR
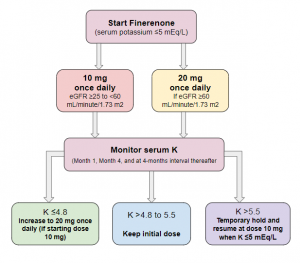
References:
-
KDIGO 2022 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR DIABETES MANAGEMENT IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE 2022 (https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/KDIGO-2022-Diabetes-Management-GL_Public-Review-draft_1Mar2022.pdf)
-
Jasleen K. Ghuman and Katherine R. Tuttle. Perspective on Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonism in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Kidney 360 April 2022, 3 (4) 744-748; DOI: https://doi.org/10.34067/KID.0007072021
-
Vlado Perkovic, MBBS, PhDSunil V Badve, MD, PhDGeorge L Bakris, MD. Treatment of diabetic kidney disease. UpToDate (Accessed on Nov, 1, 2022)


